Basic knowledge of injection molding machine
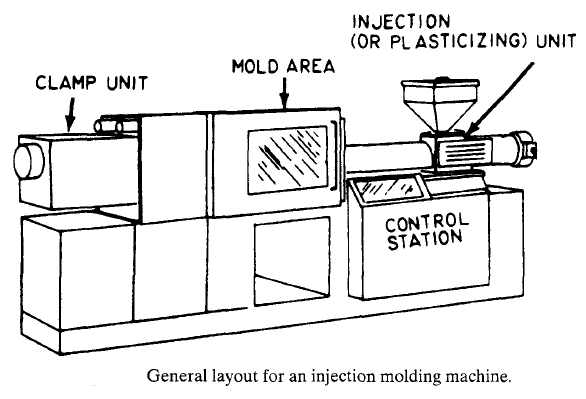
The injection molding machine (IMM) is one of the most significant and rational forming methods existing for processing plastic materials. For example, in PET packaging area, preform injection machine is an important part of whole production line. The structure of the preform injection molding machine is similar to that of the normal injection machine. A major part in this development has been by the forward-thinking machinery industry, which has been quick to seize on innovations and incorporate them into plastic molded products. The most recent examples are the all-electric and hybrid injection machine. A major focus continues to be on finding more rational means of processing the endless new plastics that are developed and also produce more cost-efficient products. A simplified general layout for an injection moulding machine is shown in the below picture.
For years so-called product innovation was the only rich source of new developments, such as reducing the number of molded product components by making them able to perform a variety of functions or by taking full use of material’s attributes. In recent years, however, process innovation has also been moving into the forefront. The latter includes all the means that help tighten up the manufacturing process, reorganizing and optimizing it. All activity is targeted for the most efficient application of production materials, a principle which must run right through the entire process from plastic materials to injection molding process, to the finished product. Even though modern injection machine with all its ingenious microprocessor control technology is in principle suited to perform flexible tasks, it nevertheless takes a whole series of peripheral auxiliary equipment to guarantee the necessary degree of flexibility.
Examples include:
(1) raw material supply systems;
(2) mold transport facilities;
(3) mold preheating banks;
(4) mold-changing devices, including rapid clamping and coupling equipment;
(5) plasticizer-cylinder-changing devices;
(6) molded-product handling equipment, particularly robots with interchangeable arms allowing adaptation to various types of production;
(7) transport systems for finished products and handling equipment to pass molded products on to subsequent production stages.
There are different types and capacities of injection molding machines to meet different product and costproduction requirements. The types are principally horizontal single clamping units with reciprocating and two-stage plasticators. They range in injection capacity (shot size) from less than an ounce to at least 400 oz (usually from 4 to 100 oz) and in clamp tonnage up to at least 10,000 tons (usual from 50 to 600 tons). Other factors when specifying an injection machine include clamp stroke, clamping speed, maximum daylight, clearances between tie rods, plasticating capacity, injection pressure, injection speed, and so on. The designer should also review regarding micro injection molding. The type and size of injection molding machine to be used are dependent on the molded product dimensions and volume, which determine the processing requirements and the shot size, as well as the required pressure and material behavior. Examples of product dimensions that directly influence the size of the machine required include all part dimensions; the number of parts to be molded in a single cycle; the mold runner system needed to produce required number of parts; the mold width, length, stack height (if stacking is used), and opening distance; and the ejector rod spacing. This information will determine the preliminary requirements for the injection molding machine.
You may also like:
- How to find a good PET injection machine manufacturer in China?
China as the world factory, there are so many different preform injection machine manufacturers. So, how to choose the right injection machine maker here is very difficult but important...
- Maintenance experience of injection molding machine
Injection molding machine is a mechanical, electronic control, hydraulic integration crystallization, electrical complex, oil pressure pipeline crossing buildings, all kinds of products...
- The FAQs about our bottle preform injection machines
What is the advantage of servo hydraulic system? 1.Independent electric screw drive brings you both melting and energy efficiency. 2.The whole hydraulic system is driven by servo...
- How to choose a injection machine?
Before you want buy a injection machine, you should know something first. We know, purchasing an injection molding machine is not a small investment, buying a too big machine is waste of m...
- How to choose a PET bottle blow molding machine?
How to buying a blow moulding machine can be a nerve racking experience for the fresh entrepreneurs. The PET bottle blow molding machine price is a secondary consideration. There countl...
Notice: The views expressed are my own and do not necessarily represent the views of DEMARK.
Copyright © 2013 - 2024 www.pet-machinery.com all rights reserved. Designed by Tina | Sitemap
